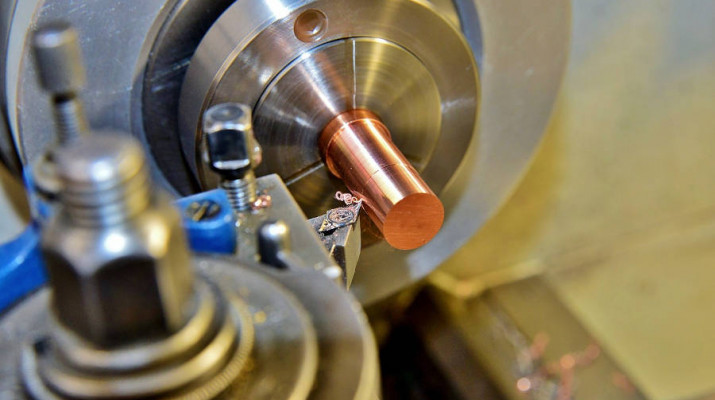
In the dynamic landscape of the metal industry, precision is a paramount consideration. The demand for high-quality, intricately designed metal components has led to the widespread adoption of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining. CNC machining has revolutionized the way metal elements are produced, offering unparalleled precision, efficiency, and versatility. This article delves into the intricacies of CNC machining and explores its pivotal role in the production of precision metal elements.
Understanding CNC Machining
What is CNC Machining?
CNC machining is a manufacturing process that utilizes computerized controls and machine tools to remove material from a workpiece, producing a custom-designed part or product. The term “Computer Numerical Control” refers to the use of programmed code to control the movements and actions of the machine tools. This technology has significantly transformed the metalworking industry, providing a level of accuracy and repeatability that traditional machining methods struggle to match.
Components of CNC Machining
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD): The process begins with the creation of a digital model using CAD software. This model serves as the blueprint for the final product.
- Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM): The CAD model is then translated into machine-readable code through CAM software. This code guides the CNC machine in executing precise movements and cuts.
- CNC Machine: The CNC machine itself is a highly sophisticated piece of equipment. It consists of various tools, such as drills, mills, and lathes, which are controlled by motors to precisely shape the raw material.
- Controller: The controller interprets the programmed code and translates it into specific movements and actions for the CNC machine.
Advantages of CNC Machining in Precision Metal Production
1. Unmatched Precision
One of the primary advantages of CNC machining is its ability to achieve unparalleled precision. The accuracy of CNC machines is measured in microns, ensuring that intricate designs and tight tolerances can be consistently met. This level of precision is crucial in industries where the smallest deviation can result in product failure.
2. Versatility in Material Selection
CNC machining is not limited to a specific type of metal. Whether it’s aluminum, steel, titanium, or exotic alloys, CNC machines can handle a wide range of materials. This versatility is essential for industries requiring diverse metal components with varying mechanical properties.
3. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Traditional machining methods often involve manual labor and are time-consuming. CNC machining, on the other hand, operates with a high degree of automation, significantly reducing production times. Additionally, CNC machines can operate continuously, 24/7, leading to increased overall efficiency and productivity.
4. Complex Geometries and Intricate Designs
The precision and automation offered by CNC machining enable the creation of complex geometries and intricate designs that would be challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional methods. This capability opens up new possibilities for innovation in product design and functionality.
5. Consistency and Repeatability
CNC machining ensures consistency in the production process. Once a program is developed and tested, it can be replicated with absolute precision across multiple workpieces. This repeatability is critical in industries where uniformity is a key requirement.
Applications of CNC Machining in Precision Metal Elements
1. Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry demands components with incredibly tight tolerances and lightweight yet robust materials. CNC machining plays a pivotal role in producing critical elements such as turbine blades, engine components, and structural parts with the precision required for safe and efficient flight.
2. Medical Devices
In the medical field, precision is non-negotiable. CNC machining is extensively used to manufacture intricate and customized components for medical devices. From orthopedic implants to surgical instruments, CNC machining ensures the highest quality and accuracy.
3. Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive industry relies heavily on CNC machining for the production of engine components, transmission parts, and intricate chassis elements. The precision offered by CNC machining contributes to the overall performance, safety, and fuel efficiency of modern vehicles.
4. Electronics and Technology
In the rapidly evolving electronics sector, miniaturization and precision are paramount. CNC machining is employed to create intricate components for electronic devices, ensuring the reliability and functionality of everything from smartphones to complex industrial electronics.
5. Tool and Die Making
The production of tools and dies requires meticulous attention to detail. CNC machining is the go-to technology for crafting molds, dies, and tooling with the precision needed for manufacturing processes in various industries.
Challenges and Considerations
While CNC machining offers a multitude of benefits, it is essential to be aware of the challenges associated with this technology:
1. Initial Investment
The acquisition and setup of CNC machines involve a significant initial investment. Small- to medium-sized enterprises may find the upfront costs challenging, although the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial financial commitment.
2. Skill Requirements
Operating and programming CNC machines requires specialized skills. Manufacturers must invest in training their workforce to maximize the potential of CNC machining. The shortage of skilled CNC operators can be a limiting factor for some companies.
3. Maintenance and Downtime
CNC machines, like any complex equipment, require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Unplanned downtime for maintenance or repairs can impact production schedules, emphasizing the need for proactive maintenance planning.
The Future of CNC Machining in Precision Metal Production
As technology continues to advance, so does the potential of CNC machining. Here are some trends shaping the future of CNC machining in the metal industry:
1. Integration of Industry 4.0 Technologies
The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and data analytics, is transforming CNC machining into a smarter and more interconnected process. Real-time monitoring and data-driven insights enhance efficiency, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production workflows.
2. Advanced Materials and Composites
As industries explore advanced materials and composites for enhanced performance, CNC machining will play a crucial role in shaping these materials with precision. From carbon fiber components to advanced metal alloys, CNC machines will adapt to the evolving landscape of material science.
3. Miniaturization and Micro-Machining
The demand for smaller, more intricate components continues to grow, especially in industries like electronics and medical devices. CNC machines are evolving to handle micro-machining with nanoscale precision, opening up new possibilities in the production of miniaturized technologies.
4. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
The incorporation of artificial intelligence into CNC machining processes is on the horizon. AI algorithms can optimize tool paths, predict machining errors, and adapt in real-time to variations in material properties, further enhancing the precision and efficiency of CNC machining.
Cornerstone of modern manufacturing
In conclusion, the use of CNC machining in the production of precision metal elements has become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. Its ability to provide unmatched precision, versatility in material selection, increased efficiency, and adaptability to diverse industries make it an indispensable technology. As we look to the future, the continued integration of advanced technologies and the exploration of new materials will further solidify CNC machining’s role in shaping the landscape of the metal industry. Embracing the potential of CNC machining is not just a choice but a strategic imperative for companies aiming to stay at the forefront of precision metal production.